Institute of Excellence in Bone Marrow Transplant
About Hospital
What is a Bone Marrow Transplant?
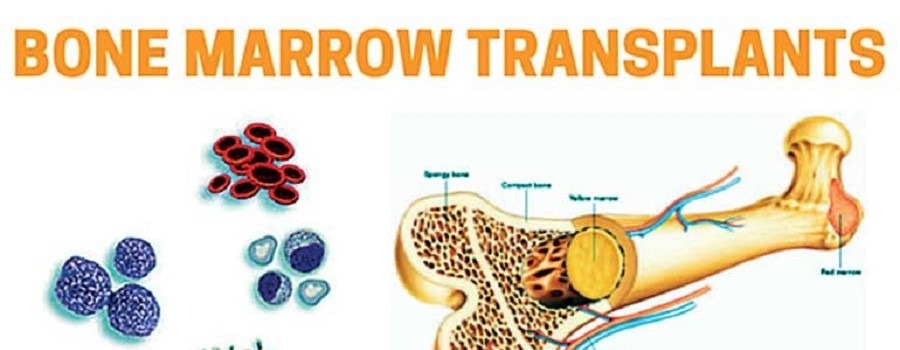
A bone marrow transplant, also known as a stem cell transplant, is a medical procedure that introduces healthy blood-forming stem cells to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow. It is commonly used to treat cancers like leukemia, multiple myeloma, lymphoma, and various blood disorders.
Previously referred to as “bone marrow transplant” due to stem cell extraction from bone marrow, modern practices now often collect stem cells from the bloodstream. In India, the procedure includes two main types: autologous transplants, using the patient’s own cells, and allogeneic transplants, using donor cells. Understanding the bone marrow transplant cost in Delhi is essential for patients seeking affordable, world-class care. Here we will share detailed info on the cost of bone marrow transplant in Delhi.
Why patients need a Bone marrow transplant?
The best bone marrow transplant doctors in India may recommend BMT for many chronic infections, diseases and for cancers as well. The recommendation of bone marrow transplant treatment depends on the health conditions of the patient. Also, bone marrow transplant success rate in India varies from patient to patient. Know the cost of bone marrow transplant in India and book your free online consultation in India.
What are the Types of Stem Cell Transplants in India?
Bone marrow transplant success rates in India have improved over the years due to progress in medical technology, highly qualified professional doctors, and better infrastructure. Here, bone marrow transplants are of two major types. Here, bone marrow transplants, also known as stem cell transplants and these transplants are of two major types.
- Autologous Bone Marrow Transplant – Autologous bone marrow transplant is a type of BMT in which a person’s own stem cells are used for the transplant. Stem cells are taken off from a person’s own body before chemotherapy or radiation treatment because a high dose of chemotherapy or radiation can cause damage to the bone marrow cells. Then stem cells are stored in a freezer. After chemotherapy or radiation treatment stem cells are put back in the patient’s body for the formation of normal blood cells.
- Allogeneic Bone Marrow Transplant – Allogeneic bone marrow transplant is a type of bone marrow transplant that involves using stem cells of a donor. Donors must be a close genetic match for stem cell transplant treatment. Often, relative is the more compatible choice of donor selection. Genetic matches can also be found from the donor registry. Specials tests are also performed to find out the perfect match for the donor for allogeneic stem cell transplant.
What is the process of collecting stem cells from the Donor?
● Bone marrow harvest – Which is a mini surgical procedure, one under general anesthesia, in which the donor will be asleep and bone marrow removed from the back of hip bones. The amount of bone marrow removed depends on the weight and on the receiving patient.
● Leukapheresis – Firstly, some shots are given to the donor to help stem cells move to the bloodstream. Using a separation machine part of white blood cells that contains stem cells are separated and removed to be later given to the recipient. The red blood cells are returned to the donor.
What Are Some Diseases That May Benefit From Bone Marrow Transplant?
Bone marrow transplantation is most commonly advantageous for the following diseases:
– Sickle cell anemia
– Leukemias
– Severe aplastic anemia
– Lymphomas
– Multiple myeloma
– Immune deficiency disorders
– Certain solid-tumor cancers, though this is less common
It is essential to recognize that the manifestation of these diseases can differ significantly among individuals, and not all patients with these conditions may be appropriate candidates for a bone marrow transplant.
How Bone Marrow Transplant Procedure is Done?
Your doctor will assess whether a bone marrow transplant is appropriate for your condition. This will involve a physical examination and various tests to evaluate your blood and the functionality of your heart, lungs, liver, and other essential organs.
If a transplant is considered a feasible option, your physician will explain the specific procedure you will undergo and what to expect throughout the process.
Process of Bone Marrow Transplant
Medical Test and Evaluation:
Patient undergo numerous test for the bone marrow transplant, this can include:
- Blood tests
- Imaging scans (e.g., X-rays, CT, or MRI)
- Heart and lung function tests
- Bone marrow biopsy
Finding the Right Donor:
A suitable donor for a bone marrow transplant is characterized by having human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that closely match those of the recipient. HLA are proteins present in the blood. Medical experts assess HLA compatibility by evaluating blood test results from potential donors and recipients, a method referred to as HLA typing. The transplant can be performed in two ways: an autologous transplant or an allogeneic transplant.
Collecting of Bone Marrow
The Transplant Phase begins with the critical step of stem cell collection. For patients undergoing an allogeneic transplant, where cells are sourced from a donor, the donor may either have a surgical procedure to harvest bone marrow or undergo apheresis to collect peripheral blood stem cells.
Bone marrow harvesting is performed under general anesthesia, requiring several small incisions in the pelvic bones to extract the marrow. In contrast, peripheral blood collection involves administering growth factor injections to the donor over several days to stimulate stem cell production, followed by the use of a specialized blood filtering device to collect the stem cells.
Once collected, the stem cells are processed in a laboratory, where they undergo rigorous testing to evaluate cell viability and ensure an adequate quantity of stem cells is present. It may also be necessary to purify the cells to remove excess red blood cells or plasma, and in some cases, specific T-cells may be eliminated to reduce the risk of graft-versus-host disease.
For autologous transplants, which utilize the patient’s own cells, the cells are typically preserved by freezing with specialized preservatives until needed. The administration of stem cells occurs through a central venous catheter, similar to a blood transfusion.
This infusion process usually lasts from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the volume of cells being infused. During this time, nursing staff closely monitor vital signs and remain alert for any potential adverse reactions. Patients may experience side effects such as nausea, chills, or chest discomfort during the infusion, all of which can be managed with appropriate medications.
Engraftment Period
The engraftment phase typically begins between days 10 and 28 following a transplant, indicated by a gradual increase in white blood cell counts. This development is a positive indicator; however, patients require close observation as their new immune system is still maturing. There is a significant risk of complications, particularly for those who have received an allogeneic transplant, as they may be susceptible to acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
As patients move beyond the initial month, the emphasis shifts to long-term recovery. While monitoring becomes less frequent, patients are still expected to attend regular check-ups for at least a year. It is essential for patients to follow stringent protective measures, including:
– Wearing masks in public environments.
– Avoiding crowded areas and contact with sick individuals.
– Adhering to a strict diet to minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses.
– Taking prescribed medications, especially immunosuppressants for those who have had allogeneic transplants.
– Participating in regular screenings to detect potential complications.
Complications And Side Effects
The complications that may arise from a bone marrow transplant can vary significantly based on several factors, including:
– The specific type of marrow transplant performed
– The underlying disease that necessitated the transplant
– The preparative regimen used prior to the transplant
– The recipient’s age and overall health status
– The level of tissue compatibility between the donor and recipient
– The presence of severe complications
It is crucial to recognize that the complications associated with a bone marrow transplant can differ greatly among individuals, with each person potentially displaying unique symptoms.
- Leukemia :
- ALL Cost: $20,000 – $25,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit
- AML Cost: $20,000 – $25,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit
- Thalassemia :
- Full Match BMT : $25,000 – $28,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit
- Half Match BMT : $35,000 – $40,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit
- Sickle Cell Anemia :
- Full Match BMT : $25,000 – $28,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.
- Half Match BMT : $35,000 – $40,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.
- Multiple Myeloma :
- Autologous BMT Cost: $20,000 – $22,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.
- Aplastic Anemia :
- Full Match BMT : $25,000 – $28,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.
- Half Match BMT : $35,000 – $40,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.
- Lymphoma (Chemotherapy & Radiation Therapy)
- Cost: $8,000 – $15,000 (depending on stage and treatment)
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (Chemotherapy & Radiation Therapy-4 to 6 cycles )
- Cost: $10,000 – $1,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) :
- Cost: $35,000 – $40,000 approx. excluding any major complication / ICU visit.

Hospital Branches
Specialty


Advance Techology

International Patient Services

Our Facilities
- Comfort: In-room TVs, Wi-Fi, private rooms, accessibility, family options, laundry, safe, dry cleaning, concierge, spa, café.
- Treatment: Medical record transfer, online consultations, rehab, pharmacy, legalization, follow-up.
- Money: Insurance coordination, currency exchange, ATM, card payments, online banking, shop.
- Language: Interpreter, translation services.
- Food: Restaurant, international cuisine, dietary options.
- Transport: Airport pickup, local tours, transport booking, visa assistance, car hire, air ambulance.
Success Stories
No Stories found.
Videos
No Videos found.
Location & Address
INDIA














